cartoframes.examples module¶
Download, preview, and query example datasets for use in cartoframes examples. Try examples by running the notebooks in binder, or trying the Example Datasets notebook.
In addition to the functions listed below, this examples module provides a
CartoContext that is
authenticated against all public datasets in the https://cartoframes.carto.com
account. This means that besides reading the datasets from CARTO, users can
also create maps from these datasets.
For example, the following will produce an interactive map of poverty rates in census tracts in Brooklyn, New York (preview of static version below code).
from cartoframes.examples import example_context from cartoframes import Layer example_context.map(Layer('brooklyn_poverty', color='poverty_per_pop'))
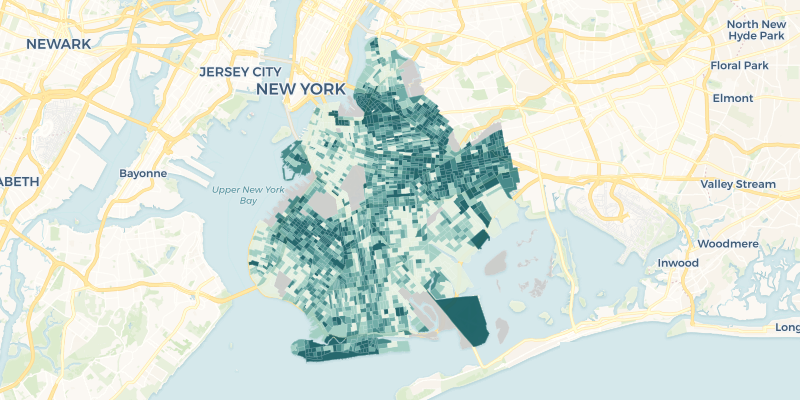
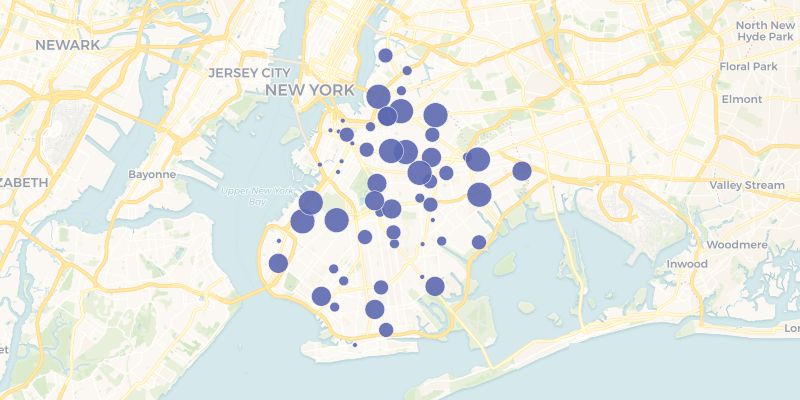
To query datasets, use the CartoContext.query method. The following example finds
the poverty rate in the census tract a McDonald’s fast food joint is located
(preview of static map below code).
from cartoframes.examples import import example_context # query to get poverty rates where mcdonald's are located in brooklyn q = ''' SELECT m.the_geom, m.cartodb_id, m.the_geom_webmercator, c.poverty_per_pop FROM mcdonalds_nyc as m, brooklyn_poverty as c WHERE ST_Intersects(m.the_geom, c.the_geom) ''' # get data df = example_context.query(q) # visualize data from cartoframes import QueryLayer example_context.map(QueryLayer(q, size='poverty_per_pop'))
To write datasets to your account from the examples account, the following is a good method:
from cartoframes import CartoContext from cartoframes.examples import read_taxi USERNAME = 'your user name' APIKEY = 'your API key' cc = CartoContext( base_url='https://{}.carto.com'.format(USERNAME), api_key=APIKEY ) cc.write( read_taxi(), 'taxi_data_examples_acct', lnglat=('pickup_latitude', 'pickup_longitude') )
-
class
cartoframes.examples.Examples¶ Bases:
cartoframes.context.CartoContextA CartoContext with a CARTO account containing example data. This special
CartoContextprovides read access to all the datasets in the cartoframes CARTO account.The recommended way to use this class is to import the example_context from the cartoframes.examples module:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_taxi()
The following tables are available for use with the
CartoContext.read,CartoContext.map, andCartoContext.querymethods.brooklyn_poverty- basic poverty information for Brooklyn, New Yorkmcdonalds_nyc- McDonald’s locations in New York Citynat- historical USA-wide homicide rates at the county levelnyc_census_tracts- Census tract boundaries for New York Citytaxi_50k- Taxi trip data, including pickup/drop-off locations. This table does not have an explicit geometry, so one must be created from the pickup_latitude/pickup_longitude columns, the dropoff_latitude/dropoff_longitude columns, or through some other process. When writing this table to your account, make sure to specify the lnglat flag inCartoContext.write
Besides the standard
CartoContextmethods, this class includes a convenience method for each of the tables listed above. See the full list below.-
data(table_name, metadata, persist_as=None, how='the_geom')¶ Get an augmented CARTO dataset with Data Observatory measures. Use CartoContext.data_discovery to search for available measures, or see the full Data Observatory catalog. Optionally persist the data as a new table.
Example
Get a DataFrame with Data Observatory measures based on the geometries in a CARTO table.
cc = cartoframes.CartoContext(BASEURL, APIKEY) median_income = cc.data_discovery('transaction_events', regex='.*median income.*', time='2011 - 2015') df = cc.data('transaction_events', median_income)
Pass in cherry-picked measures from the Data Observatory catalog. The rest of the metadata will be filled in, but it’s important to specify the geographic level as this will not show up in the column name.
median_income = [{'numer_id': 'us.census.acs.B19013001', 'geom_id': 'us.census.tiger.block_group', 'numer_timespan': '2011 - 2015'}] df = cc.data('transaction_events', median_income)
Parameters: - table_name (str) – Name of table on CARTO account that Data Observatory measures are to be added to.
- metadata (pandas.DataFrame) – List of all measures to add to
table_name. See
CartoContext.data_discoveryoutputs for a full list of metadata columns. - persist_as (str, optional) – Output the results of augmenting
table_name to persist_as as a persistent table on CARTO.
Defaults to
None, which will not create a table. - how (str, optional) – Not fully implemented. Column name for identifying the geometry from which to fetch the data. Defaults to the_geom, which results in measures that are spatially interpolated (e.g., a neighborhood boundary’s population will be calculated from underlying census tracts). Specifying a column that has the geometry identifier (for example, GEOID for US Census boundaries), results in measures directly from the Census for that GEOID but normalized how it is specified in the metadata.
Returns: A DataFrame representation of table_name which has new columns for each measure in metadata.
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Raises: - NameError – If the columns in table_name are in the
suggested_namecolumn of metadata. - ValueError – If metadata object is invalid or empty, or if the number of requested measures exceeds 50.
- CartoException – If user account consumes all of Data Observatory quota
-
data_augment(table_name, metadata)¶
-
data_boundaries(boundary=None, region=None, decode_geom=False, timespan=None, include_nonclipped=False)¶ Find all boundaries available for the world or a region. If boundary is specified, get all available boundary polygons for the region specified (if any). This method is espeically useful for getting boundaries for a region and, with
CartoContext.dataandCartoContext.data_discovery, getting tables of geometries and the corresponding raw measures. For example, if you want to analyze how median income has changed in a region (see examples section for more).Examples
Find all boundaries available for Australia. The columns geom_name gives us the name of the boundary and geom_id is what we need for the boundary argument.
import cartoframes cc = cartoframes.CartoContext('base url', 'api key') au_boundaries = cc.data_boundaries(region='Australia') au_boundaries[['geom_name', 'geom_id']]
Get the boundaries for Australian Postal Areas and map them.
from cartoframes import Layer au_postal_areas = cc.data_boundaries(boundary='au.geo.POA') cc.write(au_postal_areas, 'au_postal_areas') cc.map(Layer('au_postal_areas'))
Get census tracts around Idaho Falls, Idaho, USA, and add median income from the US census. Without limiting the metadata, we get median income measures for each census in the Data Observatory.
cc = cartoframes.CartoContext('base url', 'api key') # will return DataFrame with columns `the_geom` and `geom_ref` tracts = cc.data_boundaries( boundary='us.census.tiger.census_tract', region=[-112.096642,43.429932,-111.974213,43.553539]) # write geometries to a CARTO table cc.write(tracts, 'idaho_falls_tracts') # gather metadata needed to look up median income median_income_meta = cc.data_discovery( 'idaho_falls_tracts', keywords='median income', boundaries='us.census.tiger.census_tract') # get median income data and original table as new dataframe idaho_falls_income = cc.data( 'idaho_falls_tracts', median_income_meta, how='geom_refs') # overwrite existing table with newly-enriched dataframe cc.write(idaho_falls_income, 'idaho_falls_tracts', overwrite=True)
Parameters: - boundary (str, optional) – Boundary identifier for the boundaries
that are of interest. For example, US census tracts have a
boundary ID of
us.census.tiger.census_tract, and Brazilian Municipios have an ID ofbr.geo.municipios. Find IDs by runningCartoContext.data_boundarieswithout any arguments, or by looking in the Data Observatory catalog. - region (str, optional) –
Region where boundary information or, if boundary is specified, boundary polygons are of interest. region can be one of the following:
- table name (str): Name of a table in user’s CARTO account
- bounding box (list of float): List of four values (two
lng/lat pairs) in the following order: western longitude,
southern latitude, eastern longitude, and northern latitude.
For example, Switzerland fits in
[5.9559111595,45.8179931641,10.4920501709,47.808380127]
- timespan (str, optional) – Specific timespan to get geometries from. Defaults to use the most recent. See the Data Observatory catalog for more information.
- decode_geom (bool, optional) – Whether to return the geometries as Shapely objects or keep them encoded as EWKB strings. Defaults to False.
- include_nonclipped (bool, optional) – Optionally include non-shoreline-clipped boundaries. These boundaries are the raw boundaries provided by, for example, US Census Tiger.
Returns: If boundary is specified, then all available boundaries and accompanying geom_refs in region (or the world if region is
Noneor not specified) are returned. If boundary is not specified, then a DataFrame of all available boundaries in region (or the world if region isNone)Return type: pandas.DataFrame
- boundary (str, optional) – Boundary identifier for the boundaries
that are of interest. For example, US census tracts have a
boundary ID of
-
data_discovery(region, keywords=None, regex=None, time=None, boundaries=None, include_quantiles=False)¶ Discover Data Observatory measures. This method returns the full Data Observatory metadata model for each measure or measures that match the conditions from the inputs. The full metadata in each row uniquely defines a measure based on the timespan, geographic resolution, and normalization (if any). Read more about the metadata response in Data Observatory documentation.
Internally, this method finds all measures in region that match the conditions set in keywords, regex, time, and boundaries (if any of them are specified). Then, if boundaries is not specified, a geographical resolution for that measure will be chosen subject to the type of region specified:
- If region is a table name, then a geographical resolution that is roughly equal to region size / number of subunits.
- If region is a country name or bounding box, then a geographical resolution will be chosen roughly equal to region size / 500.
Since different measures are in some geographic resolutions and not others, different geographical resolutions for different measures are oftentimes returned.
Tip
To remove the guesswork in how geographical resolutions are selected, specify one or more boundaries in boundaries. See the boundaries section for each region in the Data Observatory catalog.
The metadata returned from this method can then be used to create raw tables or for augmenting an existing table from these measures using
CartoContext.data. For the full Data Observatory catalog, visit https://cartodb.github.io/bigmetadata/. When working with the metadata DataFrame returned from this method, be careful to only remove rows not columns as CartoContext.data <cartoframes.context.CartoContext.data> generally needs the full metadata.Note
Narrowing down a discovery query using the keywords, regex, and time filters is important for getting a manageable metadata set. Besides there being a large number of measures in the DO, a metadata response has acceptable combinations of measures with demonimators (normalization and density), and the same measure from other years.
For example, setting the region to be United States counties with no filter values set will result in many thousands of measures.
Examples
Get all European Union measures that mention
freight.meta = cc.data_discovery('European Union', keywords='freight', time='2010') print(meta['numer_name'].values)
Parameters: - region (str or list of float) –
Information about the region of interest. region can be one of three types:
- region name (str): Name of region of interest. Acceptable values are limited to: ‘Australia’, ‘Brazil’, ‘Canada’, ‘European Union’, ‘France’, ‘Mexico’, ‘Spain’, ‘United Kingdom’, ‘United States’.
- table name (str): Name of a table in user’s CARTO account
with geometries. The region will be the bounding box of
the table.
Note
If a table name is also a valid Data Observatory region name, the Data Observatory name will be chosen over the table.
- bounding box (list of float): List of four values (two
lng/lat pairs) in the following order: western longitude,
southern latitude, eastern longitude, and northern latitude.
For example, Switzerland fits in
[5.9559111595,45.8179931641,10.4920501709,47.808380127]
Note
Geometry levels are generally chosen by subdividing the region into the next smallest administrative unit. To override this behavior, specify the boundaries flag. For example, set boundaries to
'us.census.tiger.census_tract'to choose US census tracts. - keywords (str or list of str, optional) – Keyword or list of keywords in measure description or name. Response will be matched on all keywords listed (boolean or).
- regex (str, optional) – A regular expression to search the measure
descriptions and names. Note that this relies on PostgreSQL’s
case insensitive operator
~*. See PostgreSQL docs for more information. - boundaries (str or list of str, optional) – Boundary or list of boundaries that specify the measure resolution. See the boundaries section for each region in the Data Observatory catalog.
- include_quantiles (bool, optional) – Include quantiles calculations
which are a calculation of how a measure compares to all measures
in the full dataset. Defaults to
False. IfTrue, quantiles columns will be returned for each column which has it pre-calculated.
Returns: A dataframe of the complete metadata model for specific measures based on the search parameters.
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Raises: - ValueError – If region is a
listand does not consist of four elements, or if region is not an acceptable region - CartoException – If region is not a table in user account
-
read_brooklyn_poverty(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Poverty information for Brooklyn, New York, USA. See the function
read_brooklyn_povertyfor more information.Example:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_brooklyn_poverty()
-
read_mcdonalds_nyc(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ McDonald’s locations for New York City, USA. See the function
read_mcdonalds_nycfor more informationExample:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_mcdonalds_nyc()
-
read_nat(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Historical homicide rates for the United States at the county level. See the function
read_natfor more informationExample:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_nat()
-
read_ne_50m_graticules_15(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ 50m world Mercator grid <cartoframes.examples.read_ne_50m_graticules_15>` for more information.
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_ne_50m_graticules_15()
-
read_nyc_census_tracts(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Census tracts for New York City, USA. See the function
read_nyc_census_tractsfor more informationExample:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_nyc_census_tracts()
-
read_taxi(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Taxi pickup and drop-off logs for New York City, USA. See the function
read_taxifor more informationExample:
from cartoframes.examples import example_context df = example_context.read_taxi()
-
write(df, table_name, temp_dir=None, overwrite=False, lnglat=None, encode_geom=False, geom_col=None, **kwargs)¶ Write a DataFrame to a CARTO table.
Examples
Write a pandas DataFrame to CARTO.
cc.write(df, 'brooklyn_poverty', overwrite=True)
Scrape an HTML table from Wikipedia and send to CARTO with content guessing to create a geometry from the country column. This uses a CARTO Import API param content_guessing parameter.
url = 'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_life_expectancy' # retrieve first HTML table from that page df = pd.read_html(url, header=0)[0] # send to carto, let it guess polygons based on the 'country' # column. Also set privacy to 'public' cc.write(df, 'life_expectancy', content_guessing=True, privacy='public') cc.map(layers=Layer('life_expectancy', color='both_sexes_life_expectancy'))
Warning
datetime64[ns] column will lose precision sending a dataframe to CARTO because postgresql has millisecond resolution while pandas does nanoseconds
Parameters: - df (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame to write to
table_namein user CARTO account - table_name (str) – Table to write
dfto in CARTO. - temp_dir (str, optional) – Directory for temporary storage of data that is sent to CARTO. Defaults are defined by appdirs.
- overwrite (bool, optional) – Behavior for overwriting
table_nameif it exits on CARTO. Defaults toFalse. - lnglat (tuple, optional) – lng/lat pair that can be used for
creating a geometry on CARTO. Defaults to
None. In some cases, geometry will be created without specifying this. See CARTO’s Import API for more information. - encode_geom (bool, optional) – Whether to write geom_col to CARTO as the_geom.
- geom_col (str, optional) – The name of the column where geometry information is stored. Used in conjunction with encode_geom.
- **kwargs –
Keyword arguments to control write operations. Options are:
- compression to set compression for files sent to CARTO.
This will cause write speedups depending on the dataset.
Options are
None(no compression, default) orgzip. - Some arguments from CARTO’s Import API. See the params listed in the documentation for more information. For example, when using content_guessing=’true’, a column named ‘countries’ with country names will be used to generate polygons for each country. Another use is setting the privacy of a dataset. To avoid unintended consequences, avoid file, url, and other similar arguments.
- compression to set compression for files sent to CARTO.
This will cause write speedups depending on the dataset.
Options are
Returns: DatasetNote
DataFrame indexes are changed to ordinary columns. CARTO creates an index called cartodb_id for every table that runs from 1 to the length of the DataFrame.
- df (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame to write to
-
cartoframes.examples.read_brooklyn_poverty(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read the dataset brooklyn_poverty into a pandas DataFrame from the cartoframes example account at https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/brooklyn_poverty/public This dataset contains poverty rates for census tracts in Brooklyn, New York
The data looks as follows (styled on poverty_per_pop):
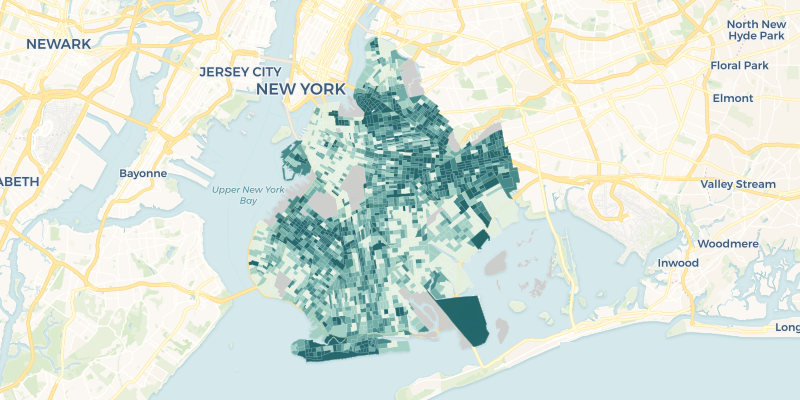
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table brooklyn_poverty on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_brooklyn_poverty df = read_brooklyn_poverty()
-
cartoframes.examples.read_mcdonalds_nyc(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read the dataset mcdonalds_nyc into a pandas DataFrame from the cartoframes example account at https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/mcdonalds_nyc/public This dataset contains the locations of McDonald’s Fast Food within New York City.
Visually the data looks as follows:
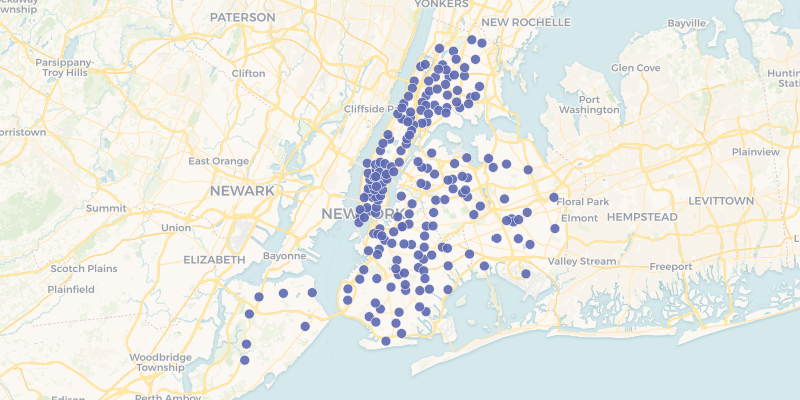
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table mcdonalds_nyc on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_mcdonalds_nyc df = read_mcdonalds_nyc()
-
cartoframes.examples.read_nat(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read nat dataset: US county homicides 1960-1990
This table is located at: https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/nat/public
Visually, the data looks as follows (styled by the hr90 column):
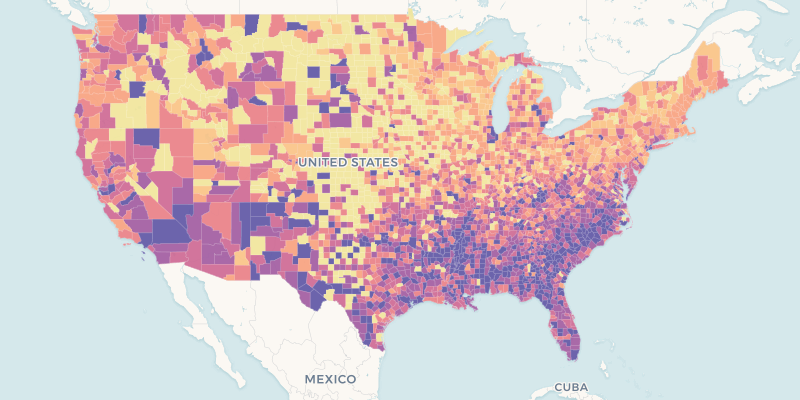
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table nat on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_nat df = read_nat()
-
cartoframes.examples.read_ne_50m_graticules_15(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read the dataset ne_50m_graticules_15 into a pandas DataFrame from the cartoframes example account at https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/ne_50m_graticules_15/public This dataset contains a 50m world Mercator grid
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table ne_50m_graticules_15 on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_ne_50m_graticules_15 df = read_ne_50m_graticules_15()
-
cartoframes.examples.read_nyc_census_tracts(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read the dataset nyc_census_tracts into a pandas DataFrame from the cartoframes example account at https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/nyc_census_tracts/public This dataset contains the US census boundaries for 2015 Tiger census tracts and the corresponding GEOID in the geom_refs column.
Visually the data looks as follows:
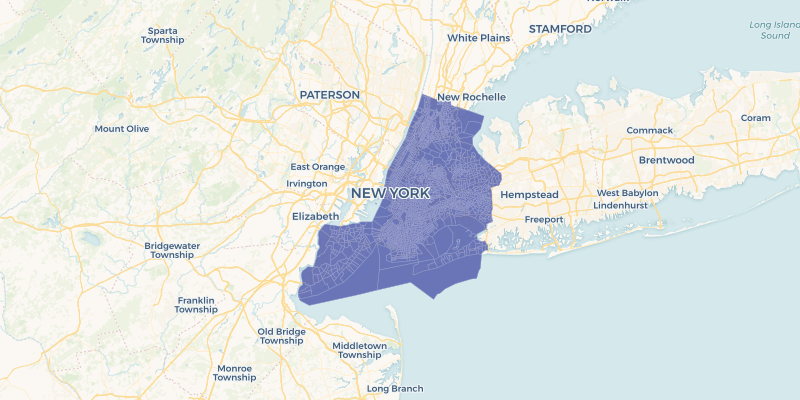
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table nyc_census_tracts on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_nyc_census_tracts df = read_nyc_census_tracts()
-
cartoframes.examples.read_taxi(limit=None, **kwargs)¶ Read the dataset taxi_50k into a pandas DataFrame from the cartoframes example account at https://cartoframes.carto.com/tables/taxi_50k/public. This table has a sample of 50,000 taxi trips taken in New York City. The dataset includes fare amount, tolls, payment type, and pick up and drop off locations.
Note
This dataset does not have geometries. The geometries have to be created by using the pickup or drop-off lng/lat pairs. These can be specified in CartoContext.write.
To create geometries with example_context.query, write a query such as this:
example_context.query(''' SELECT CDB_LatLng(pickup_latitude, pickup_longitude) as the_geom, cartodb_id, fare_amount FROM taxi_50 ''')
The data looks as follows (using the pickup location for the geometry and styling by fare_amount):
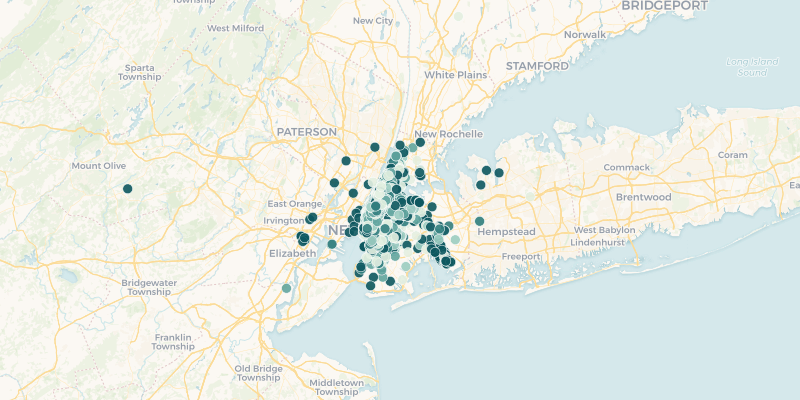
Parameters: - limit (int, optional) – Limit results to limit. Defaults to return all rows of the original dataset
- **kwargs – Arguments accepted in
CartoContext.read
Returns: Data in the table taxi_50k on the cartoframes example account
Return type: pandas.DataFrame
Example:
from cartoframes.examples import read_taxi df = read_taxi()